Adding Routing page
Learn how to add basic routing to components in an Angular application.
Overview
In this part, we will:
- Add two routes to our generated routing module
- Hook the router outlet into our markup
- Test that new routes are working
Problem
We need to set up routes for the home view and restaurant view.
What you need to know
Router Outlet
RouterOutlet is an Angular directive that is a placeholder for content that is filled when the route changes. In this example the HomeComponent template or the AboutComponent template are shown below the <router-outlet> element as the route changes.
<script src="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/rxjs/6.2.1/rxjs.umd.min.js"></script>
<script src="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/core-js/2.5.7/core.js"/></script>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/@angular/core@7.2.0/bundles/core.umd.js"/></script>
<script src="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/zone.js/0.8.26/zone.min.js"></script>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/@angular/common@7.2.0/bundles/common.umd.js"></script>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/@angular/compiler@7.2.0/bundles/compiler.umd.js"></script>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/@angular/router@7.2.0/bundles/router.umd.js"></script>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/@angular/platform-browser@7.2.0/bundles/platform-browser.umd.js"></script>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/@angular/platform-browser-dynamic@7.2.0/bundles/platform-browser-dynamic.umd.js"></script>
<script src="//unpkg.com/mock-url@^5.0.0" type="module"></script>
<mock-url pushstate:from="true"></mock-url>
<base href="/">
<my-app></my-app>
<script type="typescript">
const { Component, NgModule, VERSION } = ng.core;
const { BrowserModule } = ng.platformBrowser;
const { CommonModule } = ng.common;
const { Routes, RouterModule } = ng.router;
@Component({
selector: 'my-app',
template: `
<ul class="nav">
<li routerLinkActive="active">
<a routerLink="/about">About</a>
</li>
<li routerLinkActive="active">
<a routerLink="">Home</a>
</li>
</ul>
<router-outlet></router-outlet>
`
})
class AppComponent {
constructor() {
}
}
@Component({
selector: 'about-component',
template: `
<p>An about component!</p>
`
})
class AboutComponent {
constructor() {
}
}
@Component({
selector: 'home-component',
template: `
<p>A home component!</p>
`
})
class HomeComponent {
constructor() {
}
}
const routes: Routes = [
{ path: 'about', component: AboutComponent },
{ path: '**', component: HomeComponent }
]
@NgModule({
imports: [RouterModule.forRoot(routes)],
exports: [RouterModule]
})
class AppRoutingModule { }
@NgModule({
declarations: [AppComponent, AboutComponent, HomeComponent],
imports: [
BrowserModule,
CommonModule,
AppRoutingModule,
],
bootstrap: [AppComponent],
providers: []
})
class AppModule {}
const { platformBrowserDynamic } = ng.platformBrowserDynamic;
platformBrowserDynamic()
.bootstrapModule(AppModule)
.catch(err => console.error(err));
</script>
Router
To be able to navigate between different views in our app, we can take advantage of Angular’s built-in routing module. Angular generated src/app/app-routing.module.ts for us and included it in our root module. src/app/app-routing.module.ts currently looks like:
import { NgModule } from '@angular/core';
import { RouterModule, Routes } from '@angular/router';
const routes: Routes = [];
@NgModule({
imports: [RouterModule.forRoot(routes)],
exports: [RouterModule]
})
export class AppRoutingModule { }
The router module takes an array of routes we can generate in a few different ways that will render content in the router-outlet directive.
Setting Paths to Components
The following example will render the AboutComponent in the router-outlet when the path is /about:
<script src="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/rxjs/6.2.1/rxjs.umd.min.js"></script>
<script src="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/core-js/2.5.7/core.js"/></script>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/@angular/core@7.2.0/bundles/core.umd.js"/></script>
<script src="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/zone.js/0.8.26/zone.min.js"></script>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/@angular/common@7.2.0/bundles/common.umd.js"></script>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/@angular/compiler@7.2.0/bundles/compiler.umd.js"></script>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/@angular/router@7.2.0/bundles/router.umd.js"></script>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/@angular/platform-browser@7.2.0/bundles/platform-browser.umd.js"></script>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/@angular/platform-browser-dynamic@7.2.0/bundles/platform-browser-dynamic.umd.js"></script>
<script src="//unpkg.com/mock-url@^5.0.0" type="module"></script>
<mock-url pushstate:from="true"></mock-url>
<base href="/">
<my-app></my-app>
<script type="typescript">
const { Component, NgModule, VERSION } = ng.core;
const { BrowserModule } = ng.platformBrowser;
const { CommonModule } = ng.common;
const { Routes, RouterModule } = ng.router;
@Component({
selector: 'my-app',
template: `
<ul class="nav">
<li routerLinkActive="active">
<a routerLink="/about">About</a>
</li>
<li routerLinkActive="active">
<a routerLink="">Home</a>
</li>
</ul>
<router-outlet></router-outlet>
`
})
class AppComponent {
constructor() {
}
}
@Component({
selector: 'about-component',
template: `
<p>An about component!</p>
`
})
class AboutComponent {
constructor() {
}
}
@Component({
selector: 'home-component',
template: `
<p>A home component!</p>
`
})
class HomeComponent {
constructor() {
}
}
const routes: Routes = [
{ path: 'about', component: AboutComponent },
{ path: '**', component: HomeComponent }
]
@NgModule({
imports: [RouterModule.forRoot(routes)],
exports: [RouterModule]
})
class AppRoutingModule { }
@NgModule({
declarations: [AppComponent, AboutComponent, HomeComponent],
imports: [
BrowserModule,
CommonModule,
AppRoutingModule,
],
bootstrap: [AppComponent],
providers: []
})
class AppModule {}
const { platformBrowserDynamic } = ng.platformBrowserDynamic;
platformBrowserDynamic()
.bootstrapModule(AppModule)
.catch(err => console.error(err));
</script>
Using Wildcards
The next example uses the wildcard path, which will render the PageNotFoundComponent when any unregistered route is hit:
<script src="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/rxjs/6.2.1/rxjs.umd.min.js"></script>
<script src="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/core-js/2.5.7/core.js"/></script>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/@angular/core@7.2.0/bundles/core.umd.js"/></script>
<script src="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/zone.js/0.8.26/zone.min.js"></script>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/@angular/common@7.2.0/bundles/common.umd.js"></script>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/@angular/compiler@7.2.0/bundles/compiler.umd.js"></script>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/@angular/router@7.2.0/bundles/router.umd.js"></script>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/@angular/platform-browser@7.2.0/bundles/platform-browser.umd.js"></script>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/@angular/platform-browser-dynamic@7.2.0/bundles/platform-browser-dynamic.umd.js"></script>
<script src="//unpkg.com/mock-url@^5.0.0" type="module"></script>
<mock-url pushstate:from="true"></mock-url>
<base href="/">
<my-app></my-app>
<script type="typescript">
// app.js
const { Component, NgModule, VERSION } = ng.core;
const { BrowserModule } = ng.platformBrowser;
const { CommonModule } = ng.common;
const { Routes, RouterModule } = ng.router;
@Component({
selector: 'my-app',
template: `
<p>Look at me!</p>
<ul class="nav">
<li routerLinkActive="active">
<a routerLink="/about">About</a>
</li>
<li routerLinkActive="active">
<a routerLink="/merp">/merp - Not an actual route</a>
</li>
<li routerLinkActive="active">
<a routerLink="/blarg">/blarg - Another not actual route</a>
</li>
</ul>
<router-outlet></router-outlet>
`
})
class AppComponent {
constructor() {
}
}
@Component({
selector: 'about-component',
template: `
<p>An about component!</p>
`
})
class AboutComponent {
constructor() {
}
}
@Component({
selector: 'unfound-component',
template: `
<p>These are not the components you are looking for.</p>
`
})
class PageNotFoundComponent {
constructor() {
}
}
const routes: Routes = [
{ path: 'about', component: AboutComponent },
{ path: '', redirectTo: '/about', pathMatch: 'full' },
{ path: '**', component: PageNotFoundComponent }
];
@NgModule({
imports: [RouterModule.forRoot(routes)],
exports: [RouterModule]
})
class AppRoutingModule { }
@NgModule({
declarations: [AppComponent, AboutComponent, PageNotFoundComponent],
imports: [
BrowserModule,
CommonModule,
AppRoutingModule,
],
bootstrap: [AppComponent],
providers: []
})
class AppModule {}
const { platformBrowserDynamic } = ng.platformBrowserDynamic;
platformBrowserDynamic()
.bootstrapModule(AppModule)
.catch(err => console.error(err));
</script>
Redirecting Routes
This example shows one route redirecting to another:
<script src="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/rxjs/6.2.1/rxjs.umd.min.js"></script>
<script src="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/core-js/2.5.7/core.js"/></script>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/@angular/core@7.2.0/bundles/core.umd.js"/></script>
<script src="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/zone.js/0.8.26/zone.min.js"></script>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/@angular/common@7.2.0/bundles/common.umd.js"></script>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/@angular/compiler@7.2.0/bundles/compiler.umd.js"></script>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/@angular/router@7.2.0/bundles/router.umd.js"></script>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/@angular/platform-browser@7.2.0/bundles/platform-browser.umd.js"></script>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/@angular/platform-browser-dynamic@7.2.0/bundles/platform-browser-dynamic.umd.js"></script>
<script src="//unpkg.com/mock-url@^5.0.0" type="module"></script>
<mock-url pushstate:from="true"></mock-url>
<base href="/">
<my-app></my-app>
<script type="typescript">
// app.js
const { Component, NgModule, VERSION } = ng.core;
const { BrowserModule } = ng.platformBrowser;
const { CommonModule } = ng.common;
const { Routes, RouterModule } = ng.router;
@Component({
selector: 'my-app',
template: `
<p>Look at me!</p>
<ul class="nav">
<li routerLinkActive="active">
<a routerLink="/about">About</a>
</li>
<li routerLinkActive="active">
<a routerLink="/merp">Not an actual route</a>
</li>
<li routerLinkActive="active">
<a routerLink="/blarg">Another not actual route</a>
</li>
<li routerLinkActive="active">
<a routerLink="team">/team - I will reroute to /about</a>
</li>
</ul>
<router-outlet></router-outlet>
`
})
class AppComponent {
constructor() {
}
}
@Component({
selector: 'about-component',
template: `
<p>An about component!</p>
`
})
class AboutComponent {
constructor() {
}
}
@Component({
selector: 'unfound-component',
template: `
<p>These are not the components you are looking for.</p>
`
})
class PageNotFoundComponent {
constructor() {
}
}
const routes: Routes = [
{ path: 'about', component: AboutComponent },
{ path: 'team', redirectTo: '/about', pathMatch: 'full' },
{ path: '**', component: PageNotFoundComponent }
];
@NgModule({
imports: [RouterModule.forRoot(routes)],
exports: [RouterModule]
})
class AppRoutingModule { }
@NgModule({
declarations: [AppComponent, AboutComponent, PageNotFoundComponent],
imports: [
BrowserModule,
CommonModule,
AppRoutingModule,
],
bootstrap: [AppComponent],
providers: []
})
class AppModule {}
const { platformBrowserDynamic } = ng.platformBrowserDynamic;
platformBrowserDynamic()
.bootstrapModule(AppModule)
.catch(err => console.error(err));
</script>
Setting Paths to Modules
As our applications grow, it doesn’t make sense to load all the code at once. Thanks to lazy loading, we can wait to render modules until a specific route requiring them is hit.
const routes: Routes = [
{ path: 'about', component: AboutComponent },
{ path: 'team', redirectTo: '/about', pathMatch: 'full' },
{
path: 'products',
loadChildren: () => {
return import('./products/products.module').then(m => m.ProductsModule);
}
},
{ path: '**', component: PageNotFoundComponent }
];
@NgModule({
imports: [RouterModule.forRoot(routes)],
exports: [RouterModule]
})
class AppRoutingModule { }
<base-href>
In our index.html file, the angular cli included <base href="/>. This isn’t an Angular specific feature and you can read more about it here, but it’s important to know this is how the Angular router will know how to compose URLs - the value in the href attribute specifies the base URL for all relative URLs contained in the app. If you’d like to serve your app from a different directory (wherever the index.html will be served from) or have a specific hosting URL that your app will be deployed at, you will need to change the base href to match.
<!doctype html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>PlaceMyOrder</title>
<base href="/">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1">
<link rel="icon" type="image/x-icon" href="favicon.ico">
</head>
<body>
<pmo-root></pmo-root>
</body>
</html>
Technical requirements
Create routes for the HomeComponent and RestaurantComponent. When the route is "", the HomeComponent should display, and when the route is /restaurants the RestaurantComponent should display. These changes should be made in src/app/app-routing.module.ts.
Notice that you will be able to click the Choose a Restaurant button after implementing the solution:
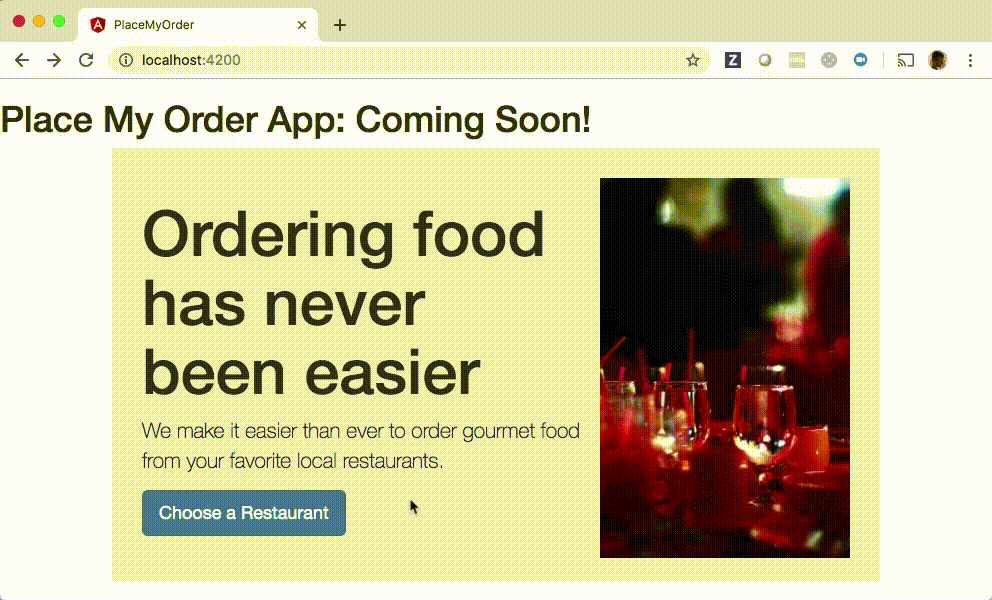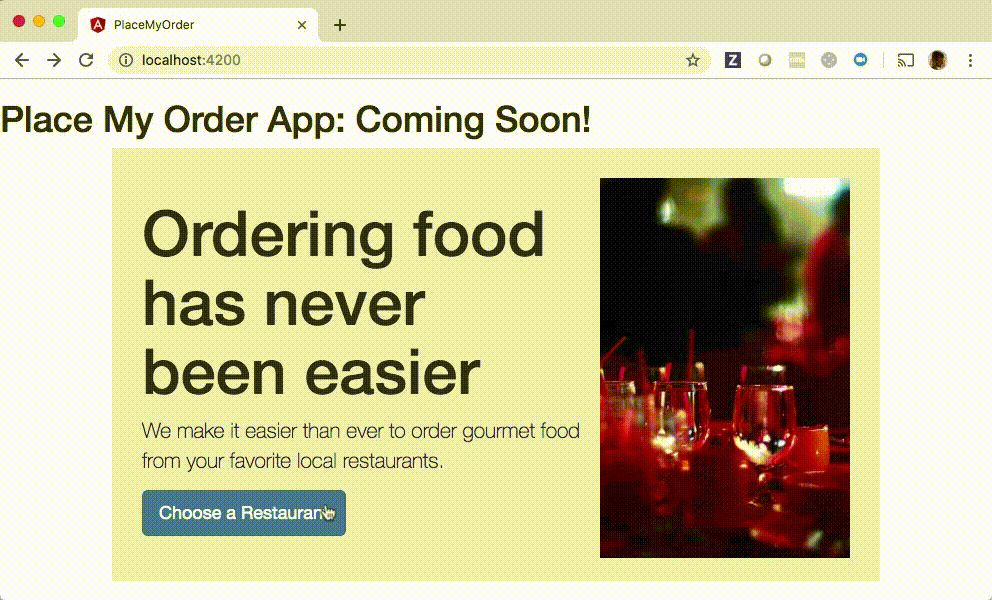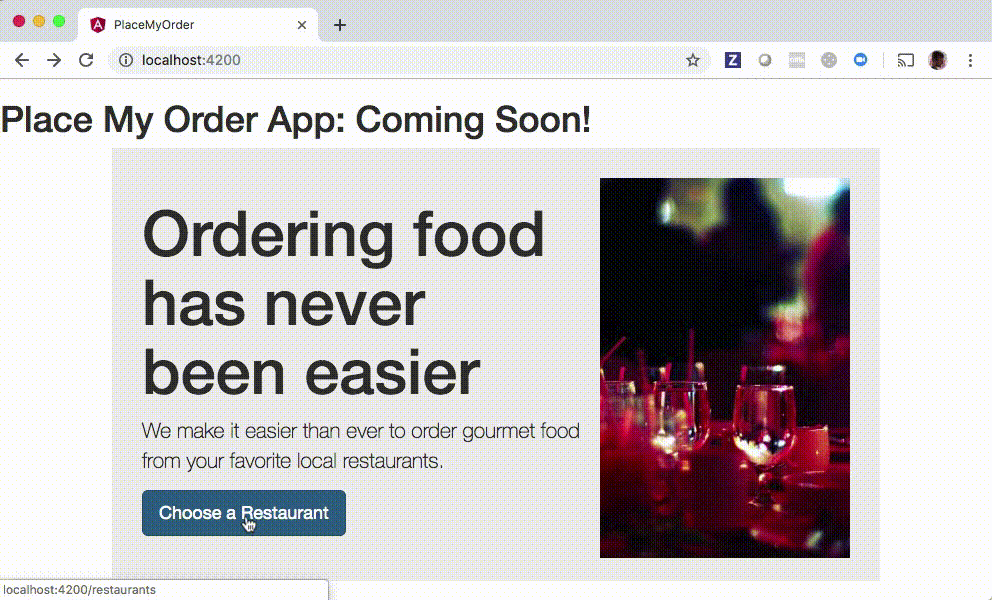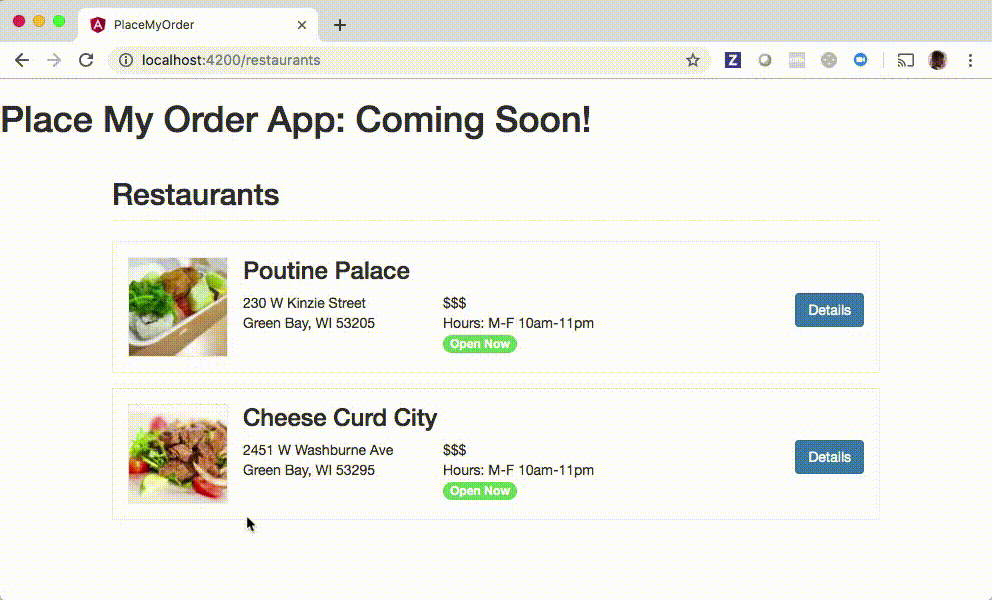
Setup
<router-outlet>, which handles routing to a component based on a url, was added to our src/app/app.component.html file when we first generated our app. But since that time, we added components to that view. Let’s remove those components because <router-outlet> will handle showing
those components going forward.
✏️ Update src/app/app.component.html to:
<h1>Place My Order App: Coming Soon!</h1>
<router-outlet />
How to verify your solution is correct
If you have completed the exercise successfully you should be able to see the home component when the app loads, and the restaurant component when you navigate to localhost:4200/restaurants. You may have noticed the routerLink attribute on the <a> tag in our home component markup. This one of the ways we link to specific routes in our app. When you click that link, you should see the restaurants component.
<a class="btn" routerLink="/restaurants" role="button"> Choose a Restaurant </a>
✏️ Update the spec file src/app/app.component.spec.ts to be:
import { Location } from '@angular/common';
import { NO_ERRORS_SCHEMA } from '@angular/core';
import { ComponentFixture, fakeAsync, TestBed } from '@angular/core/testing';
import { Router } from '@angular/router';
import { AppRoutingModule } from './app-routing.module';
import { AppComponent } from './app.component';
import { HomeComponent } from './home/home.component';
import { RestaurantComponent } from './restaurant/restaurant.component';
describe('AppComponent', () => {
let fixture: ComponentFixture<AppComponent>;
beforeEach(async () => {
await TestBed.configureTestingModule({
imports: [AppRoutingModule],
declarations: [AppComponent, HomeComponent, RestaurantComponent],
schemas: [NO_ERRORS_SCHEMA],
}).compileComponents();
fixture = TestBed.createComponent(AppComponent);
});
it('should create the app', () => {
const app = fixture.componentInstance;
expect(app).toBeTruthy();
});
it(`should have as title 'place-my-order'`, () => {
const app = fixture.componentInstance;
expect(app.title).toEqual('place-my-order');
});
it('should render title in a h1 tag', () => {
fixture.detectChanges();
const compiled = fixture.nativeElement as HTMLElement;
expect(compiled.querySelector('h1')?.textContent).toContain(
'Place My Order App: Coming Soon!'
);
});
it('should render the HomeComponent with router navigates to "/" path', fakeAsync(() => {
const location: Location = TestBed.inject(Location);
const router: Router = TestBed.inject(Router);
fixture.detectChanges();
const compiled = fixture.nativeElement as HTMLElement;
router.navigate(['']).then(() => {
expect(location.path()).toBe('');
expect(compiled.querySelector('pmo-home')).not.toBe(null);
});
}));
it('should render the RestaurantsComponent with router navigates to "/restaurants" path', fakeAsync(() => {
const location: Location = TestBed.inject(Location);
const router: Router = TestBed.inject(Router);
fixture.detectChanges();
const compiled = fixture.nativeElement as HTMLElement;
router.navigate(['restaurants']).then(() => {
expect(location.path()).toBe('/restaurants');
expect(compiled.querySelector('pmo-restaurant')).not.toBe(null);
});
}));
});
Solution
If you’ve implemented the solution correctly, the tests will pass when you run npm run test!
Click to see the solution
✏️ Update src/app/app-routing.module.ts to:import { NgModule } from '@angular/core';
import { RouterModule, Routes } from '@angular/router';
import { HomeComponent } from './home/home.component';
import { RestaurantComponent } from './restaurant/restaurant.component';
const routes: Routes = [
{
path: '',
component: HomeComponent,
},
{
path: 'restaurants',
component: RestaurantComponent,
},
];
@NgModule({
imports: [RouterModule.forRoot(routes)],
exports: [RouterModule],
})
export class AppRoutingModule {}